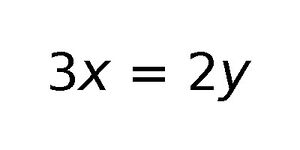Algebra (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:3x=2y.jpg|thumb|A simple algebraic equation: 3''x'' = 3''y''.]]'''Algebra''' (from Arabic "al-jabr" meaning "reunion of broken parts") is one of the broad parts of [[Mathematics (nonfiction)|mathematics]], together with [[Number theory (nonfiction)|number theory]], [[Geometry|geometry]], and [[Mathematical analysis (nonfiction)|analysis]]. | [[File:3x=2y.jpg|thumb|A simple algebraic equation: 3''x'' = 3''y''.]]'''Algebra''' (from Arabic "al-jabr" meaning "reunion of broken parts") is one of the broad parts of [[Mathematics (nonfiction)|mathematics]], together with [[Number theory (nonfiction)|number theory]], [[Geometry (nonfiction)|geometry]], and [[Mathematical analysis (nonfiction)|analysis]]. | ||
In its most general form, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. As such, it includes everything from elementary equation solving to the study of abstractions such as groups, rings, and fields. | In its most general form, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. As such, it includes everything from elementary equation solving to the study of abstractions such as groups, rings, and fields. | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Boolean algebra (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Equality (nonfiction)]] | * [[Equality (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Equation solving (nonfiction)]] | * [[Equation solving (nonfiction)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:48, 14 December 2017
Algebra (from Arabic "al-jabr" meaning "reunion of broken parts") is one of the broad parts of mathematics, together with number theory, geometry, and analysis.
In its most general form, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. As such, it includes everything from elementary equation solving to the study of abstractions such as groups, rings, and fields.
The more basic parts of algebra are called elementary algebra; the more abstract parts are called abstract algebra or modern algebra. Elementary algebra is generally considered to be essential for any study of mathematics, science, or engineering, as well as such applications as medicine and economics.
Elementary algebra differs from arithmetic in the use of abstractions, such as using letters to stand for numbers that are either unknown or allowed to take on many values. For example, x+2=5 the letter x is unknown, but the law of inverses can be used to discover its value: x=3. In E = mc2, the letters E and m are variables, and the letter c is a constant, the speed of light in a vacuum.
Algebra gives methods for solving equations and expressing formulas that are much easier (for those who know how to use them) than the older method of writing everything out in words.
The word algebra is also used in certain specialized ways. A special kind of mathematical object in abstract algebra is called an "algebra", and the word is used, for example, in the phrases linear algebra and algebraic topology.
A mathematician who does research in algebra is called an algebraist.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Boolean algebra (nonfiction)
- Equality (nonfiction)
- Equation solving (nonfiction)
- Mathematics (nonfiction)
- Variable (nonfiction)
External links:
- Algebra @ Wikipedia
- How to Understand Algebra @ WikiHow
- Objectives: Solve, Simplify, Factor, Reduce
- Learn the difference between “expression” and “equation.”
- Learn PEMDAS. In algebra, the steps you take must occur in a logical order, which is called the “order of operations.” This is often simplified by the mnemonic device “PEMDAS.” The letters of PEMDAS will help you know which operations to perform in order. The letters of PEMDAS stand for:
Parentheses. Exponents. Multiplication. Division. Addition. Subtraction.