Template:Selected anniversaries/September 25: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
||1929 – Jimmy Doolittle performs the first blind flight from Mitchel Field proving that full instrument flying from take off to landing is possible. | ||1929 – Jimmy Doolittle performs the first blind flight from Mitchel Field proving that full instrument flying from take off to landing is possible. | ||
||Paul Ehrenfest (b. September 25, 1933) was an Austrian and Dutch theoretical physicist, who made major contributions to the field of statistical mechanics and its relations with quantum mechanics, including the theory of phase transition and the Ehrenfest theorem. | |||
||Adrien Douady (b. September 1935) was a French mathematician. | ||Adrien Douady (b. September 1935) was a French mathematician. | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
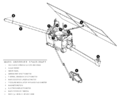
File:Mars Observer diagram.png|link=Mars Observer (nonfiction)|1992: NASA launches the [[Mars Observer (nonfiction)|Mars Observer]], a $511 million probe to [[Mars (nonfiction)|Mars]], in the first U.S. mission to the planet in 17 years. The probe will fail eleven months later. | File:Mars Observer diagram.png|link=Mars Observer (nonfiction)|1992: NASA launches the [[Mars Observer (nonfiction)|Mars Observer]], a $511 million probe to [[Mars (nonfiction)|Mars]], in the first U.S. mission to the planet in 17 years. The probe will fail eleven months later. | ||
|| | ||Robert W (Bob) Floyd (d. September 25, 2001) was an eminent computer scientist. His contributions include the design of the Floyd–Warshall algorithm (independently of Stephen Warshall), which efficiently finds all shortest paths in a graph, Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm for detecting cycles in a sequence, and his work on parsing. In one isolated paper he introduced the important concept of error diffusion for rendering images, also called Floyd–Steinberg dithering (though he distinguished dithering from diffusion). A significant achievement was pioneering the field of program verification using logical assertions with the 1967 paper Assigning Meanings to Programs. This was an important contribution to what later became Hoare logic. | ||
File:Humpty Dumpty At Bat.jpg|link=Humpty Dumpty At Bat|2002: Steganographic analysis of ''[[Humpty Dumpty At Bat]]'' reveals previously unknown biography of Babe Ruth by [[Lewis Carroll (nonfiction)|Lewis Carroll]]. | File:Humpty Dumpty At Bat.jpg|link=Humpty Dumpty At Bat|2002: Steganographic analysis of ''[[Humpty Dumpty At Bat]]'' reveals previously unknown biography of Babe Ruth by [[Lewis Carroll (nonfiction)|Lewis Carroll]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:09, 3 December 2017
1644: Astronomer and instrument maker Ole Rømer born. He will make the first quantitative measurements of the speed of light.
1789: The United States Congress passes twelve amendments to the United States Constitution: The Congressional Apportionment Amendment (which was never ratified), the Congressional Compensation Amendment, and the ten that are known as the Bill of Rights.
1845: Judge Havelock With Glass is "a reasonably accurate depiction of events as I experienced them," according to the Judge.
1893: Mathematician and statistician Harald Cramér born. He will help found probability theory as a branch of mathematics, writing in 1926: "The probability concept should be introduced by a purely mathematical definition, from which its fundamental properties and the classical theorems are deduced by purely mathematical operations."
1992: NASA launches the Mars Observer, a $511 million probe to Mars, in the first U.S. mission to the planet in 17 years. The probe will fail eleven months later.
2002: Steganographic analysis of Humpty Dumpty At Bat reveals previously unknown biography of Babe Ruth by Lewis Carroll.
2003: Journalist, writer, literary editor, and actor George Plimpton dies.
2017: Dennis Paulson of Mars says that the twenty-fifth anniversary of the launch of the Mars Observer is a bittersweet event, because the spacecraft will be lost eleven months later.