Template:Selected anniversaries/July 1: Difference between revisions
From Gnomon Chronicles
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
||1968 – The Nuclear non-proliferation treaty is signed in Washington, D.C., London and Moscow by sixty-two countries. | ||1968 – The Nuclear non-proliferation treaty is signed in Washington, D.C., London and Moscow by sixty-two countries. | ||
|| | ||Sir William Lawrence Bragg CH, OBE, MC, FRS (d. 1 July 1971) was an Australian-born British physicist and X-ray crystallographer, discoverer (1912) of Bragg's law of X-ray diffraction, which is basic for the determination of crystal structure. He was joint winner (with his father, William Henry Bragg) of the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1915 | ||
File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|2001: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] dies. He did fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics. | File:Nikolay Basov.jpg|link=Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|2001: Physicist and educator [[Nikolay Basov (nonfiction)|Nikolay Basov]] dies. He did fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics. | ||
Revision as of 19:19, 4 November 2017
1646: Mathematician and philosopher Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz born. He will develop differential and integral calculus independently of Isaac Newton, and design and build mechanical calculators.
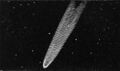
1819: Johann Georg Tralles discovers the Great Comet of 1819 (C/1819 N1). It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by François Arago.
1888: Mathematician and physicist Johann Jakob Balmer develops a Gnomon algorithm function based on the visible spectral lines of the hydrogen atom which unexpectedly reveals imminent crimes against mathematical constants.
2001: Physicist and educator Nikolay Basov dies. He did fundamental work in the field of quantum electronics.
2017: The Custodian says he is "not planning on retiring any time soon."