Template:Selected anniversaries/September 18: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
|File:Bartolomeu Lourenço de Gusmão.jpg|link=Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|1701: Inventor and priest [[Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|Bartolomeu de Gusmão]]'s uses [[Gnomon algorithm]] to design improved [[Airship (nonfiction)|airship]]. | |File:Bartolomeu Lourenço de Gusmão.jpg|link=Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|1701: Inventor and priest [[Bartolomeu de Gusmão (nonfiction)|Bartolomeu de Gusmão]]'s uses [[Gnomon algorithm]] to design improved [[Airship (nonfiction)|airship]]. | ||
||1709 – Samuel Johnson, English lexicographer and poet (d. 1784) | |||
File:Pieter van Musschenbroek.jpg|link=Pieter van Musschenbroek (nonfiction)|1751: Mathematician, astronomer, and crime-fighter [[Pieter van Musschenbroek (nonfiction)|Pieter van Musschenbroek]] uses a grid of Leyden jars to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | File:Pieter van Musschenbroek.jpg|link=Pieter van Musschenbroek (nonfiction)|1751: Mathematician, astronomer, and crime-fighter [[Pieter van Musschenbroek (nonfiction)|Pieter van Musschenbroek]] uses a grid of Leyden jars to detect and prevent [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | ||
||1752 – Adrien-Marie Legendre, French mathematician and theorist (d. 1833) | |||
File:Leonhard Euler.jpg|link=Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|1783: Mathematician and physicist [[Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|Leonhard Euler]] dies. He made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function. | File:Leonhard Euler.jpg|link=Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|1783: Mathematician and physicist [[Leonhard Euler (nonfiction)|Leonhard Euler]] dies. He made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function. | ||
||1809 – The Royal Opera House in London opens. | ||1809 – The Royal Opera House in London opens. | ||
||1819 – Léon Foucault, French physicist and academic (d. 1868) | |||
||1851 – First publication of The New-York Daily Times, which later becomes The New York Times. | ||1851 – First publication of The New-York Daily Times, which later becomes The New York Times. | ||
||1860 – Joseph Locke, English engineer and politician (b. 1805) | |||
||1873 – Panic of 1873: The U.S. bank Jay Cooke & Company declares bankruptcy, triggering a series of bank failures. | ||1873 – Panic of 1873: The U.S. bank Jay Cooke & Company declares bankruptcy, triggering a series of bank failures. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 23: | ||
File:Wizard Jan Kochanowski.jpg|link=Jan_Kochanowski|1888: Poet and wizard [[Jan Kochanowski]] adapts [[Nebra sky disk (nonfiction)|Nebra sky disk]] for use as [[scrying engine]]. | File:Wizard Jan Kochanowski.jpg|link=Jan_Kochanowski|1888: Poet and wizard [[Jan Kochanowski]] adapts [[Nebra sky disk (nonfiction)|Nebra sky disk]] for use as [[scrying engine]]. | ||
||1896 – Hippolyte Fizeau, French physicist and academic (b. 1819) | |||
||1907 – Edwin McMillan, American physicist and chemist, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1991) | |||
||1908 – Victor Ambartsumian, Georgian-Armenian astrophysicist, astronomer, and academic (d. 1996) | |||
||1928 – Juan de la Cierva makes the first autogyro crossing of the English Channel. | ||1928 – Juan de la Cierva makes the first autogyro crossing of the English Channel. | ||
||1931 – The Mukden Incident gives Japan a pretext to invade and occupy Manchuria. | ||1931 – The Mukden Incident gives Japan a pretext to invade and occupy Manchuria. | ||
||1932 – Nikolay Rukavishnikov, Russian physicist and astronaut (d. 2002) | |||
||1934 – The USSR is admitted to the League of Nations. | ||1934 – The USSR is admitted to the League of Nations. | ||
||1939 – Jan Camiel Willems, Belgian mathematician and theorist (d. 2013) | |||
||1947 – The National Security Council and the Central Intelligence Agency are established in the United States under the National Security Act. | ||1947 – The National Security Council and the Central Intelligence Agency are established in the United States under the National Security Act. | ||
| Line 31: | Line 49: | ||
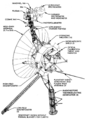
File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] takes first photograph of the Earth and the Moon together. | File:Voyager spacecraft diagram.png|link=Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|1977: [[Voyager 1 (nonfiction)|Voyager 1]] takes first photograph of the Earth and the Moon together. | ||
||1977 – Paul Bernays, English-Swiss mathematician and philosopher (b. 1888) | |||
||1980 – Soyuz 38 carries two cosmonauts (including one Cuban) to Salyut 6 space station. | ||1980 – Soyuz 38 carries two cosmonauts (including one Cuban) to Salyut 6 space station. | ||
Revision as of 17:45, 14 August 2017
1751: Mathematician, astronomer, and crime-fighter Pieter van Musschenbroek uses a grid of Leyden jars to detect and prevent crimes against mathematical constants.
1783: Mathematician and physicist Leonhard Euler dies. He made important and influential discoveries in many branches of mathematics, and introduced much of the modern mathematical terminology and notation, such as the notion of a mathematical function.
1888: Poet and wizard Jan Kochanowski adapts Nebra sky disk for use as scrying engine.
1967: Physicist, academic, and Nobel Prize laureate John Cockcroft dies. He was instrumental in the development of nuclear power.
1977: Voyager 1 takes first photograph of the Earth and the Moon together.
2017: The Custodian tells a funny story about why you can't go in there.