Algorithm (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
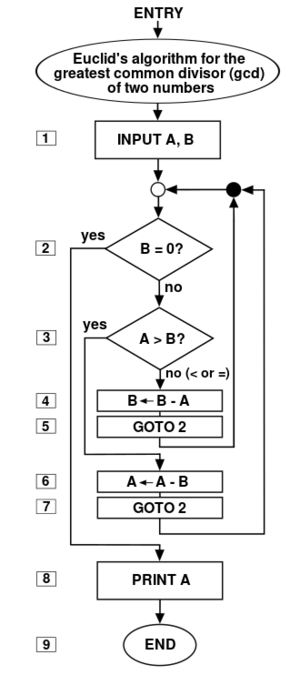
In [[ | [[File:Euclid's_algorithm.svg|thumb|Flow chart of an algorithm (Euclid's algorithm) for calculating the greatest common divisor (g.c.d.) of two numbers a and b in locations named A and B. The algorithm proceeds by successive subtractions in two loops: IF the test B ≥ A yields "yes" (or true) (more accurately the number b in location B is greater than or equal to the number a in location A) THEN, the algorithm specifies B ← B − A (meaning the number b − a replaces the old b). Similarly, IF A > B, THEN A ← A − B. The process terminates when (the contents of) B is 0, yielding the g.c.d. in A.]]In [[Mathematics (nonfiction)|mathematics]] and [[Computer science (nonfiction)|Computer science]], an '''algorithm''' is a self-contained step-by-step set of operations to be performed. | ||
== Quotations == | |||
Cory Doctorow on Rob Smith's ''Rage Inside the Machine'': | |||
<blockquote>Smith shows how the parts of machine learning that do work refute some of the uglier philosophical ideas that have risen in currency as algorithms have taken over our society -- just as the Victorians had their "blind watchmaker," the rise of evolutionary algorithms has given a new lease on life to eugenic theories about survival of the fittest and the need to purify and protect the "best" among us.</blockquote> | |||
Source: [https://boingboing.net/2019/06/26/kids-mag-highlights-for-c.html Rage Inside the Machine: an insightful, brilliant critique of AI's computer science, sociology, philosophy and economics] by Cory Doctorow @ Boing Boing | |||
== In the News == | |||
<gallery> | |||
File:Ascleplius Myrmidon Halting Problem.jpg|link=On Halting Problems|Asclepius Myrmidon publishes new analysis of unregistered [[On Halting Problems|halting problem algorithms]], predicts emergence of new algorithms for [[crimes against mathematical constants]]. | |||
File:Numbered cake pops.jpg|link=Numbered cake algorithm|[[Numbered cake algorithm]] used to build new type of [[scrying engine]]. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Fiction cross-reference == | |||
* [[Gnomon Algorithm]] | |||
* [[Mathematics]] | |||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Computer science (nonfiction)]] | * [[Computer science (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Breadth-first search (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Depth-first search (nonfiction)]] | |||
* [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | * [[Mathematics (nonfiction)]] | ||
* [[Prim's algorithm (nonfiction)]] - a greedy algorithm that finds a minimum spanning tree for a weighted undirected graph | |||
* [[Theory of computation (nonfiction)]] | |||
Publications: | |||
* ''Numerical Recipes'' - a series of books on algorithms and numerical analysis by William H. Press, Saul A. Teukolsky, William T. Vetterling and Brian P. Flannery. In various editions, the books have been in print since 1986. The most recent edition was published in 2007. | |||
On the web: [http://numerical.recipes/ numerical.recipes]. | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithm Algorithm] @ Wikipedia | * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithm Algorithm] @ Wikipedia | ||
* [http://fiftyexamples.readthedocs.io/en/latest/algorithms.html Background: Algorithms] @ 50 Examples | |||
* [https://freedom-to-tinker.com/2017/05/31/what-does-it-mean-to-ask-for-an-explainable-algorithm/ What does it mean to ask for an “explainable” algorithm?] by Ed Felten | |||
* [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lwfDPtUP2P8 Ruff Ruffman, Humble Media Genius | Algorithms Sing-Along Music Video | PBS KIDS] @ YouTube | |||
[[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | [[Category:Nonfiction (nonfiction)]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:41, 3 November 2024
In mathematics and Computer science, an algorithm is a self-contained step-by-step set of operations to be performed.
Quotations
Cory Doctorow on Rob Smith's Rage Inside the Machine:
Smith shows how the parts of machine learning that do work refute some of the uglier philosophical ideas that have risen in currency as algorithms have taken over our society -- just as the Victorians had their "blind watchmaker," the rise of evolutionary algorithms has given a new lease on life to eugenic theories about survival of the fittest and the need to purify and protect the "best" among us.
Source: Rage Inside the Machine: an insightful, brilliant critique of AI's computer science, sociology, philosophy and economics by Cory Doctorow @ Boing Boing
In the News
Asclepius Myrmidon publishes new analysis of unregistered halting problem algorithms, predicts emergence of new algorithms for crimes against mathematical constants.
Numbered cake algorithm used to build new type of scrying engine.
Fiction cross-reference
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Computer science (nonfiction)
- Breadth-first search (nonfiction)
- Depth-first search (nonfiction)
- Mathematics (nonfiction)
- Prim's algorithm (nonfiction) - a greedy algorithm that finds a minimum spanning tree for a weighted undirected graph
- Theory of computation (nonfiction)
Publications:
- Numerical Recipes - a series of books on algorithms and numerical analysis by William H. Press, Saul A. Teukolsky, William T. Vetterling and Brian P. Flannery. In various editions, the books have been in print since 1986. The most recent edition was published in 2007.
On the web: numerical.recipes.
External links
- Algorithm @ Wikipedia
- Background: Algorithms @ 50 Examples
- What does it mean to ask for an “explainable” algorithm? by Ed Felten
- Ruff Ruffman, Humble Media Genius | Algorithms Sing-Along Music Video | PBS KIDS @ YouTube