Tephigram (nonfiction): Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Fiction cross-reference == | == Fiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Gnomon algorithm]] | |||
* [[Gnomon Chronicles]] | |||
* [[Tephigram]] - one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in computational weather engineering. | * [[Tephigram]] - one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in computational weather engineering. | ||
== Nonfiction cross-reference == | == Nonfiction cross-reference == | ||
* [[Napier Shaw (nonfiction)]] - inventor of the tephigram. | |||
* [[Nomogram (nonfiction)]] - a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a [[mathematical function (nonfiction)]]. | * [[Nomogram (nonfiction)]] - a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a [[mathematical function (nonfiction)]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:49, 4 March 2019
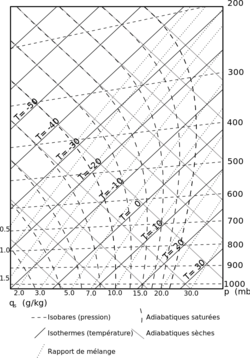
A tephigram is one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in weather analysis and forecasting.
The name evolved from the original name "T-Theta-gram" to describe the axes of temperature (T) and entropy used to create the plot.
Usually, temperature and dew point data from radiosondes are plotted on these diagrams to allow calculations of convective stability or convective available potential energy (CAPE).
Wind barbs are often plotted at the side of a tephigram to indicate the winds at different heights.
In the News
Fiction cross-reference
- Gnomon algorithm
- Gnomon Chronicles
- Tephigram - one of four thermodynamic diagrams commonly used in computational weather engineering.
Nonfiction cross-reference
- Napier Shaw (nonfiction) - inventor of the tephigram.
- Nomogram (nonfiction) - a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function (nonfiction).
External links:
- Tephigram @ Wikipedia