Template:Selected anniversaries/August 8: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
||117: Trajan dies ... Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared by the Senate optimus princeps ("the best ruler"), Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presided over the greatest military expansion in Roman history, leading the empire to attain its maximum territorial extent by the time of his death. He is also known for his philanthropic rule, overseeing extensive public building programs and implementing social welfare policies, which earned him his enduring reputation as the second of the Five Good Emperors. Pic: bust. | |||
||1492 | ||1492: Matteo Tafuri born ... alchemist. Pic: https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matteo_Tafuri | ||
||1533 | ||1533: Lucas van Leyden dies ... artist. | ||
||1555 | File:Oronce Finé.jpg|link=Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|1555: Mathematician and cartographer [[Oronce Finé (nonfiction)|Oronce Finé]] dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing [[Judicial astrology (nonfiction)|judicial astrology]]. | ||
File: | File:Uraniborg main building.jpg|link=Uraniborg (nonfiction)|1576: The cornerstone for Tycho Brahe's [[Uraniborg (nonfiction)|Uraniborg observatory]] is laid on the island of Hven. | ||
|| | ||1627: Joseph Moxon born ... hydrographer to Charles II, was an English printer specialising in mathematical books and maps, a maker of globes and mathematical instruments, and mathematical lexicographer. He produced the first English language dictionary devoted to mathematics, and the first detailed instructional manual for printers. In November 1678, he became the first tradesman to be elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1694: Antoine Arnauld dies ... was a French Roman Catholic theologian, philosopher and mathematician. Pic. | ||
|| | ||1748: Johann Friedrich Gmelin born ... naturalist, botanist, entomologist, herpetologist and malacologist. Pic. | ||
||1779: Benjamin Silliman born ... chemist and science educator. He was one of the first American professors of science, at Yale College, the first person to distill petroleum in America, and a founder of the American Journal of Science, the oldest continuously published scientific journal in the United States. Pic. | |||
File:Sir Francis Ronalds.jpg|link=Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer [[Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|Francis Ronalds]] dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph. | File:Sir Francis Ronalds.jpg|link=Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer [[Francis Ronalds (nonfiction)|Francis Ronalds]] dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph. | ||
||1876 | ||1876: Thomas Edison receives a patent for his mimeograph. TO_DO | ||
||1879 | ||1879: Bob Smith born ... physician and surgeon, co-founded Alcoholics Anonymous. | ||
||1896: George Dawson Preston born ... physicist specializing in crystallography and the structure of alloys. He was one of the first to use x-rays and electron diffraction to study the crystal structure of metals and alloys. He gives his name to the Guinier-Preston zone, discovered in 1938. Pic search. | |||
|| | ||1897: Viktor Meyer dies ... chemist and significant contributor to both organic and inorganic chemistry. He is best known for inventing an apparatus for determining vapour densities, the Viktor Meyer apparatus, and for discovering thiophene, a heterocyclic compound. Pic. | ||
|| | File:David Hilbert.jpg|link=David Hilbert (nonfiction)|1900: [[David Hilbert (nonfiction)|David Hilbert]] delivers his famous "Mathematical problems" address: "We hear within us the perpetual call: There is a problem. Seek its solution. You can find it by pure reason, for in mathematics there is no 'ignorabimus'." | ||
|| | ||1901: Ernest Lawrence born ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate (d. 1958). Pic. | ||
|| | ||1902: Paul Dirac born ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. | ||
|| | File:Edwin_Henry_Spanier_(1986).jpg|link=Edwin Spanier (nonfiction)|1921: Mathematician and academic [[Edwin Spanier (nonfiction)|Edwin Spanier]] born. Spanier will contribut to algebraic topology, co-inventing Spanier–Whitehead duality and Alexander–Spanier cohomology; also, his book on algebraic topology will become a standard textbook of its day. | ||
||1946 | ||1929: The German airship Graf Zeppelin begins a round-the-world flight. | ||
||1946: First flight of the Convair B-36, the world's first mass-produced nuclear weapon delivery vehicle, the heaviest mass-produced piston-engined aircraft, with the longest wingspan of any military aircraft, and the first bomber with intercontinental range. | |||
File:Plumbbob-Stokes barrage balloon.jpg|link=Stokes (nonfiction)|1957: A day after the [[Stokes (nonfiction)|Stokes nuclear weapon test]], large numbers of [[carnivorous dirigibles]] unexpectedly die. | File:Plumbbob-Stokes barrage balloon.jpg|link=Stokes (nonfiction)|1957: A day after the [[Stokes (nonfiction)|Stokes nuclear weapon test]], large numbers of [[carnivorous dirigibles]] unexpectedly die. | ||
|| | ||1969: Otmar Freiherr von Verschuer dies ... biologist and eugenicist. Pic. | ||
|| | File:Nixon April-29-1974.jpg|link=Watergate scandal (nonfiction)|1974: President Richard Nixon, in a nationwide television address, announces his [[Watergate scandal (nonfiction)|resignation from the office of the President of the United States]] effective noon the next day. | ||
|| | ||1979: Jacob Lionel Bakst Cooper dies ... mathematician who worked in operator theory, transform theory, thermodynamics, functional analysis and differential equations. Pic. | ||
||1987 | ||1987: Danilo Blanuša dies ... mathematician and physicist. Pic search. | ||
||1989 | ||1989: Space Shuttle program: STS-28 Mission: Space Shuttle Columbia takes off on a secret five-day military mission. | ||
||1996 | ||1996: Nevill Francis Mott dies ... physicist and academic, Nobel Prize laureate. Pic. | ||
||1998: Laszlo Szabo dies ... chess player. Pic (chess!). | |||
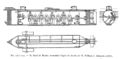
File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|2000: Confederate submarine [[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]] is raised to the surface after 136 years on the ocean floor and 30 years after its discovery by undersea explorer E. Lee Spence. | File:Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley.jpg|link=H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|2000: Confederate submarine [[H. L. Hunley (nonfiction)|H. L. Hunley]] is raised to the surface after 136 years on the ocean floor and 30 years after its discovery by undersea explorer E. Lee Spence. | ||
File:Genesis spacecraft in collection mode.jpg|link=Genesis (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|2001: NASA launches its unmanned spacecraft ''[[Genesis (spacecraft) (nonfiction)|Genesis]]''. The return capsule will crash-land in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevents the deployment of its drogue parachute. | |||
File:Fay Ajzenberg-Selove.jpg|link=Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|2012: Nuclear physicist [[Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|Fay Ajzenberg-Selove]] dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei. | File:Fay Ajzenberg-Selove.jpg|link=Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|2012: Nuclear physicist [[Fay Ajzenberg-Selove (nonfiction)|Fay Ajzenberg-Selove]] dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei. | ||
||2016: Klaus Weber dies ... scientist who made many fundamentally important contributions to biochemistry, cell biology, and molecular biology. Pic. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:04, 7 February 2022
1555: Mathematician and cartographer Oronce Finé dies. He was imprisoned in 1524, probably for practicing judicial astrology.
1576: The cornerstone for Tycho Brahe's Uraniborg observatory is laid on the island of Hven.
1873: Scientist, inventor, and engineer Francis Ronalds dies. He was knighted for creating the first working electric telegraph.
1900: David Hilbert delivers his famous "Mathematical problems" address: "We hear within us the perpetual call: There is a problem. Seek its solution. You can find it by pure reason, for in mathematics there is no 'ignorabimus'."
1921: Mathematician and academic Edwin Spanier born. Spanier will contribut to algebraic topology, co-inventing Spanier–Whitehead duality and Alexander–Spanier cohomology; also, his book on algebraic topology will become a standard textbook of its day.
1957: A day after the Stokes nuclear weapon test, large numbers of carnivorous dirigibles unexpectedly die.
1974: President Richard Nixon, in a nationwide television address, announces his resignation from the office of the President of the United States effective noon the next day.
2000: Confederate submarine H. L. Hunley is raised to the surface after 136 years on the ocean floor and 30 years after its discovery by undersea explorer E. Lee Spence.
2001: NASA launches its unmanned spacecraft Genesis. The return capsule will crash-land in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevents the deployment of its drogue parachute.
2012: Nuclear physicist Fay Ajzenberg-Selove dies. She did important experimental work in nuclear spectroscopy of light elements, authoring annual reviews of the energy levels of light atomic nuclei.